
When the choice is about exterior decoration of a house, it is very important to decide which facade for cladding your house will be the best solution: ‘wet’ or ventilated?
We will try to tell you about the strengths and weaknesses of each of the facades as detailed as possible and provide your choice in favor of one or another option.
Facade plaster (‘wet facade’)
This material has been used in construction for a long time. It acquired such popularity due to the fact that there was no alternative on the market. At the moment facade plaster allows you to simulate the look and structure of any material. Besides there are also ready mixes on the market, which significantly simplify the preparation of the plastering works. Plaster can be painted in any color, at the request of the customer. However the essential weakness of this material is its dependence on weather conditions at installation. At temperatures from -10°C and below, as well as from +30°C and above, facade plastering is prohibited, as opposed to siding, which hasn’t seasonality in work processes.
As a rule, the following is used as a thermal insulation layer:
● Styrofoam
● Extruded polystyrene foam
● Basalt wool.
Advantages of this method:
● One of the cheapest way of insulation
● For finishing the facade – any decor according to customer preferences
● Small weight
● Simple installation
Disadvantages of this method:
● Short-lived. On average, repairs are needed after 3-5 years;
● Works can only be performed at a positive air temperature;
● Specific recommendations regarding the humidity of the ambient air;
● The presence of smooth walls;
● In case of damage – expensive restoration of a ‘pie’;
● For owners of private houses – rodents spoil the material;
● Non-compliance with recommendations about work performance reduces quality of its implementation;
● At compliance of all requirements of a ‘pie’ technology cost increases;
● High requirements to the professionalism of the assembly team;
● The cost of work is higher than at installation of a ventilated facade.
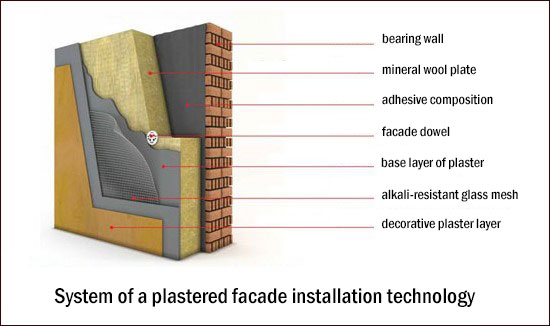
Depends on the look plasters, which are using at finishing ‘wet’ facade, there are three groups:
1. Smooth – tinted in mass or painted after application and grinding.
2. Textured – plaster mixes with visible mineral granules.
3. Factured – the relief is formed due to the special packing of the plastic mass. They are single-layer and multi-layer, monochrome and tinted.
Materials for ‘wet’ facade:
• Cement compounds – are using for finishing big surfaces. The facade is finished with cement plaster, it’s necessary to paint it for outdoor work.
• Silicate compounds (mineral plasters) – the composition is based on liquid glass. As additives use quartz sand and mineral chips, which determine strength and texture of finished facade.
• Acrylic and silicone plasters – used at finishing facades of low-rise buildings.
Technology of external finishing of ‘wet’ facade
1. Preparation processing of facade
Surface defects repairs, applying a primer and installing a plinth profile. The plinth profile serves as a support for a thermal insulation layer.
2. Insulation the prepared surface.
Cement based glue is applied on walls and after heat-proofing panels are applied on it. The panels use styrofoam, expanded polystyrene, basalt wool.
3. Mechanical fixation of insulation.
As a fixator use disc dowels.
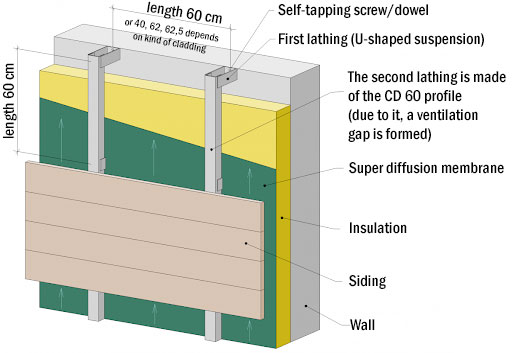
Hinged ventilated facade
Hinged ventilated facade for the house is a unique construction of cladding of the facade of the building, which consists of a few main elements, among which subsystem or framework is the most important. Framework can be made of galvanized steel, wood and other materials.
Subsystem includes not only metal elements, but also all manner of fasteners in the form of dowels, anchors, hardware, etc. With fastener elements, a layer of external cladding, namely: metal siding, siding of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or polypropylene, wood, porcelain stoneware, fiber cement etc., is installed over the framework.
Main characteristics and advantages of this method are:
● Unique design
● Good soundproofing
● Providing reliable protection of a private house from moisture
● Installation work at any time of the year
● Low load on the supporting structures of the facade
● Effective thermal insulation
● Fire safety
● Weathering of moisture from the insulation while preserving the properties of the insulation itself
Main feature of the ventilated facade is air gap, which provides preservation of natural ventilation of wall fencing.
The component parts of a facade sandwich consist of:
- Protective and decorative material, which can be chosen from variety colors and it’s fastened with metal crews to the crate (cladding);
- Framework with fasteners;
- Insulation layer;
- Ventilation gap.
Types of cladding:
● PVC(polyvinyl chloride); Polypropylene
● Metal
● Wood
● Aluminium panels
● Ceramic sand panels
● fiber cement
Installation technology of ventilated facade
1. Installing of framework, which mounted with brackets on the walls;
2. Into the cells of the frame thermal insulation is laid. At using mineral based materials we receive good vapor permeability and low flammability.
3. After this, above insulation, windproof membrane fits (for blow-out protection). The membrane has one-side vapor permeability: it releases moisture outside, but doesn’t let it inside the thermal insulation layer.
4. At finishing, mount the vertical and horizontal profiles, on which decorative trim is attached.
One of the most important parts of any ventilated facade is an insulation layer. It provides comfortable temperatures indoors and allows to save energy costs required for normal house operation. It is recommended to use in a thermal insulation layer only non-combustible materials.
The most effective insulation for ventilated facade:
● Basalt wool
● Glass wool
They are made from the environmentally friendly natural materials using heat treatment and completely with technical requirements. Styrofoam isn’t recommended while installing ventilated facades. It burns with the release of toxic materials and doesn’t allow the condensate to air out.
Ventilated facades are the most demanded and advanced from the technical point of view. Compared with other kinds of insulation, the use of flammable insulation isn’t allowed in ventilated facades. Panel and hinged ventilated facades are considered to be the most safe, subject to technology and material requirements.
Advantages of ventilated facade
● Installation of hinged ventilated structure allows you to hide all defects of main facade;
● Multilayer structure provides effective thermal insulation, waterproofing and blow-out protection;
● Using strong materials for finishing increases the resistance of the facade to external factors and prolongs its service life;
Siding or plaster, what’s cheaper?
Work with siding is significantly easier and more convenient, than with facade plaster. If you decide to make a facade with a few variants of siding, we recommend you to buy materials from one manufacturer company, Alta-Profile Ukraine. In comparison to prices, foam/polystyrene foam plaster will cost you less than siding, but such characteristics like longevity, color fastness, thermal insulation properties of siding will be higher and more reliable.
Comparative table of characteristics of hinged ventilated facade and decorative plaster (heat-insulating material – polystyrene)
| Characteristics | Hinged ventilated facades | Styrofoam/decorative plaster |
| Service life | To 50 years without repair | To 20 years, needs periodic repair |
| Installation convenience | Easy and fast installation at any time of the year. All elements made with high accuracy on factory | Requires qualified installation, excluding the appearance of cold bridges. Requires preparation of tha facade. Installation Only at a positive temperature. |
| Thermal insulation properties | Good | Good |
| Soundproofing properties | Excellent acoustic isolation | Satisfying acoustic isolation |
| Fire safety | Insulation refers to the group of non-combustible materials. Panels don’t keep burning | Styrofoam panels are susceptible to burning at the influence of open flame. Combustion products are highly toxic. Plaster does role of flame shield (if it isn’t violated) |
| Hygiene | During service life, materials fully meet hygiene requirements | During long service life, appearance of toxic decomposition products of styrofoam is possible |
| Vapor permeability | High. Condensate is removed, the house breathes | Low, environment moisturizes, which reduces thermal insulation characteristics |
| Strength | High impact strength of siding at any operation temperature from -50 to +60℃ of the external air | Fragility and probability of partly spontaneity destroying at temperatures of +80℃ (what is possible under plaster) and higher. Destroyed at impact of organic solvents |
| Color fastness | High color fastness of siding | Changing (burnout) the color of plaster |
| Biostability | Material isn’t affectable to microflora impact | Appearance of fungus and rodents is possible |
| Ease of use | Doesn’t require special care during 25 years | Requires periodic repair and replacement after 5-10 years |
Ventilated facade differs from ‘wet’ in the 2-3 cm air gap between insulation and trim panels. Such a feature of the hinged system allows it to efficiently remove moisture and condensate because of upward convection currents, which are arising behind the cladding. Therefore, the ventilated facade technology deletes moisture from insulation naturally.
Examples of calculation of ventilated facade (siding) and ‘wet’ facade (plaster)
Price of ‘wet’ finishing includes adhesive mixture, insulation and facade plaster. The cost of the ventilated facade includes insulation, hinged system and cladding. Wherein cladding and fastening system – the most expensive elements.
| Siding | Price hrn/sq. m, without work | Ready-made plaster | Price hrn/sq. m, without work |
| Alta-siding + internal ‘Cake’+styrofoam | 449 | Plaster with styrofoam | 320,7 |
| Alta-siding + internal ‘Cake’+glass wool | 604 | Plaster with basalt | 585,7 |
| Alta-siding + internal ‘Cake’+basalt | 654 | Plaster with mineral wool | 475,7 |
| Dry plaster | Price hrn/sq. m, without work | ||
| Facade panels + internal ‘Cake’+styrofoam | 1045 | Plaster with styrofoam | 261,7 |
| Facade panels + internal ‘Cake’+glass wool | 1200 | Plaster with basalt | 526,7 |
| Facade panels + internal ‘Cake’+basalt | 1250 | Plaster with mineral wool | 416,7 |
| Plaster ‘for painting’ | Price hrn/sq. m, without work | ||
| BlockHouse oak + internal ‘Cake’+styrofoam | 575 | Plaster with styrofoam | 221.9 |
| BlockHouse oak + internal ‘Cake’+glass wool | 730 | Plaster with basalt | 486.9 |
| BlockHouse oak + internal ‘Cake’+basalt | 780 | Plaster with mineral wool | 376.9 |
The choice always depends on you, but it’s necessary to consider all characteristics and advantages of one material (siding) over another (plaster). Sometimes it’s worth paying a little more and receiving quality and long-term results than renovating the facade each 2-3 years.
Select facing materials:
• Siding
• Facade panels
• Fastening system




